The Fascinating Origins of the Kurdish People: A Journey Through Time
- Kurdish History

- Jul 15, 2025
- 6 min read

The Kurdish people, known for their rich culture and history, have a story that stretches across millennia. Their heritage is a tapestry woven with threads of resilience, struggle, and vibrant tradition. This article delves into kurdish history, exploring the origins of the Kurdish people, the significance of their culture, and the pivotal moments that have shaped their identity.
Who Are the Kurdish People?
The Kurdish people are an ethnic group primarily found in a region known as Kurdistan, which spans across parts of Turkey, Iraq, Iran, and Syria. The Kurdish population is estimated to be around 30 to 40 million, making them one of the largest ethnic groups in the world without a state of their own. This unique positioning has led to a diverse and rich cultural existence that manifests deeply within kurdistan culture and heritage.
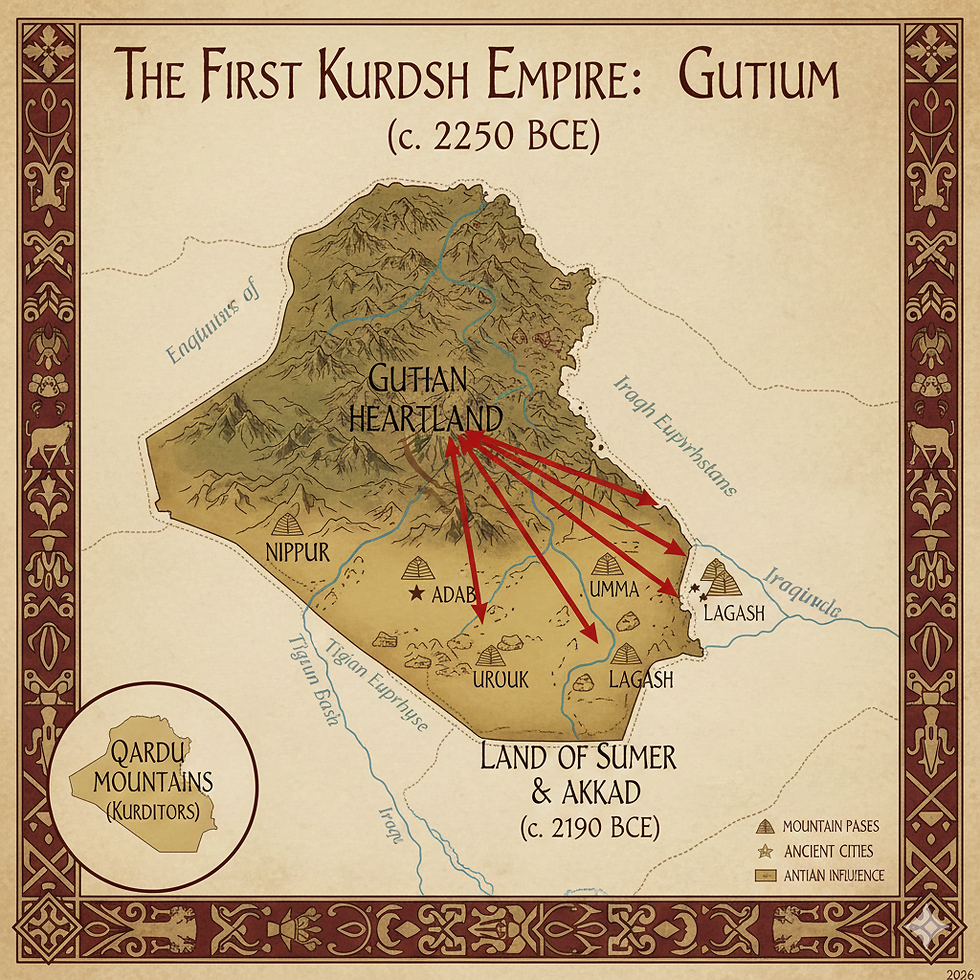
Early Origins in Ancient Civilizations
The roots of the Kurds can be traced back to ancient civilizations. Historical evidence suggests that the Kurds descend from various ancient peoples who settled in the Zagros Mountains of what is now modern-day Iran. This area was inhabited by the Medes, an ancient Iranian people, around the 7th century BC. The Medes played a crucial role in the fall of the Assyrian Empire, and their legacy is considered pivotal in kurdish history.
Additionally, the Kurds are likely linked to other groups, such as the Hurrians and the Mitanni. The language spoken by the Kurds, Kurdish, belongs to the Northwestern Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian language family, further establishing their connection to ancient tribes and nations.
Formation of a Distinct Kurdish Identity
As history progressed, the Kurdish people began to cultivate a distinct identity. By the Middle Ages, they had established various principalities characterized by local governance and distinct cultural practices. Historical figures like kurdish historical figures such as Sheikh Ahmad al-Yaqubi in the 17th century played significant roles in shaping Kurdish attitudes toward unity and identity.
The establishment of these principalities laid down the foundations for the Kurdish people’s social structures, including their tribal systems and cultural traditions. During this time, kurdish culture and heritage started to flourish, incorporating elements such as traditional music, dance, and weaving, reflecting the rich tapestry of their history through art.
Religious Diversity
The Kurdish people practice a variety of religions, including Islam (both Sunni and Shia), Yarsanism, and Zoroastrianism. The diversity in beliefs has contributed to a rich cultural heritage, with religious festivals and customs becoming integral to the Kurdish identity. Understanding these religious practices enhances appreciation for the complexities of kurdistan culture and heritage.
The Impact of Ottoman and Persian Empires
The rise of the Ottoman Empire saw Kurds living under the rule of various powers, which would continue to shape kurdish history for centuries. The Ottomans recognized the Kurds as a significant group and often utilized the tribal leaders of the Kurdish principalities as local governors. This relationship was pivotal — while it allowed for a degree of autonomy, it also placed Kurds in complex political scenarios.
Similarly, the Safavid Empire in Persia sought to exert influence over Kurdish regions, further entrenching the divisions within Kurdistan. These power dynamics initiated kurdish historical movements and diplomacy that urged the Kurdish populace to navigate their identity amidst foreign rule. The merging of political and cultural realms established rich dialogues about the essence of being Kurdish.
The 20th Century and the Struggle for Identity
The 20th century was marked by significant challenges and movements within Kurdish communities as the concept of nation-states solidified in the Middle East. The aftermath of World War I and the Treaty of Sèvres in 1920 initially promised autonomy for the Kurds. However, the subsequent Treaty of Lausanne in 1923 denied this autonomy, an event that would dictate Kurdish aspirations for the decades to follow.
This era brought forth notable kurdish public figures and leaders who became symbols of the Kurdish struggle. Figures like Mustafa Barzani emerged as prominent leaders advocating for Kurdish rights and sovereignty. They played pivotal roles in various uprisings against the oppressive regimes of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Syria.
The Role of Kurdish Historical Movements
Throughout the 20th century, numerous kurdish historical movements and diplomacy aimed to achieve greater autonomy or independence. These movements were often met with harsh crackdowns, leading to significant uprisings, such as the Kurdish revolt in Iraq during the 1960s and 70s. The notion of self-determination ignited the aspirations of many Kurds, resulting in an identity deeply intertwined with political strife.
Despite the setbacks, these movements cultivated a resilient spirit among the Kurdish people, reinforcing their desire to celebrate their culture and heritage amidst adversity. The narratives of resistance became highly celebrated, illustrating the collective spirit and unity of the Kurdish populace.
Literature and Arts: A Cultural Revival
In the face of political tension, the Kurdish people have continued to express themselves through literature, music, and the arts. Today, Kurdish writers and artists have gained recognition globally, contributing to a renaissance of kurdistan culture and heritage. Poets like Sherko Bekas and musicians such as Ibrahim Tatlıses have become prominent figures, showcasing the richness of Kurdish stories and traditions.
A Time of Change: Contemporary Kurdish Identity
The 21st century has brought both opportunities and challenges for the Kurdish people as they continue to navigate through regional complications. The fight against the Islamic State (ISIS) in Iraq and Syria showcased the bravery and tenacity of Kurdish forces, drawing international attention to their plight and resilience.
The emergence of Kurdish autonomy in the Iraqi Federal Government post-2014 marks a historical turning point that emphasizes the critical need for enduring discussions surrounding political representation and cultural rights. Today’s kurdish public figures, including political leaders like Nechirvan Barzani, play vital roles in navigating both local and international politics, thus influencing the contemporary Kurdish narrative.
The Future of Kurdish Heritage
As we look toward the future, the rediscovery and celebration of kurdish culture and heritage become paramount. The infusion of the diaspora’s revitalization efforts — which includes the global sharing of Kurdish art, literature, and educational initiatives — provides a fresh avenue for empowerment. It is through these practices that the Kurdish identity can continually evolve while firmly holding onto its roots.
The movement towards unity and cultural appreciation can also influence newer generations of Kurds, instilling a sense of pride in their unique identity and history. As more kurdish historical figures, writers, and public figures emerge, they will serve as the voices of a vibrant community committed to preserving their legacy.
A Legacy of Resilience and Pride
The story of the Kurdish people is one of resilience and determination. From ancient civilizations to modern-day narratives, the journey is imbued with rich cultural significance and historical depth. As the Kurds continue to fight for representation and recognition, their diverse history and cultural practices remain a testament to their identity.
Embracing the past while stepping boldly into the future, the Kurdish people embody a mosaic of traditions that withstand the tests of time. The origins of the Kurdish people remind us of the enduring spirit of humanity and the importance of understanding and celebrating each cultural identity that contributes to our shared world. The journey doesn’t end here; it’s an ongoing narrative that invites us all to explore and engage with the vibrant tapestry that is Kurdish heritage.
FAQs
Who are the Kurdish people?
The Kurdish people are an ethnic group primarily found in a region known as Kurdistan, which spans parts of Turkey, Iraq, Iran, and Syria, with an estimated population of 30 to 40 million.
What are the early origins of the Kurdish people?
The roots of the Kurds can be traced back to ancient civilizations in the Zagros Mountains, particularly descending from the Medes, an ancient Iranian people.
How did the Kurdish identity form over time?
The Kurdish people began to cultivate a distinct identity during the Middle Ages, establishing various principalities and cultural practices, which laid down the foundations for their social structures.
What impact did the Ottoman and Persian Empires have on the Kurds?
The rise of the Ottoman and Persian Empires shaped Kurdish history by placing them under various rules, leading to complex political dynamics and affecting their cultural and social structures.
What is the current state of Kurdish identity in the 21st century?
The 21st century has brought both opportunities and challenges for the Kurds, including the fight against ISIS and the emergence of Kurdish autonomy, emphasizing political representation and cultural rights.



Comments